Unlocking the Secrets of Memory: Neuroscientists Reveal Brain's Learning Rules!
2025-04-18
Author: Rajesh
Every day, whether you're picking up a new skill, trying out a friend's recipe, or catching up on global news, your brain is hard at work, creating memories that can last a lifetime. But have you ever wondered how your brain accomplishes this remarkable task?
The Brain's Learning Mechanism
In groundbreaking research published in the journal Science, neuroscientists have unveiled some fascinating "rules" that govern how our brains learn and form memories.
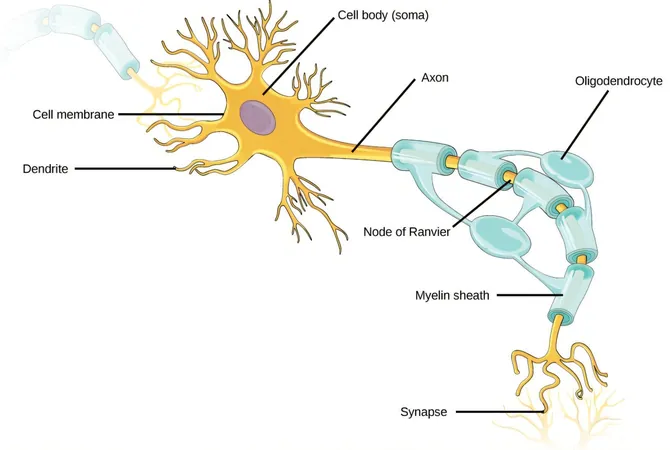
The human brain is a complex network made up of billions of nerve cells, or neurons, which transmit information through electrical pulses similar to binary code in computers. These pulses communicate across tiny connections called synapses, enabling a sophisticated exchange of information.
Neurons: The Building Blocks of Memory
Neurons have long branching extensions known as dendrites, capable of receiving thousands of inputs from other cells. The collective activity of these pulses across specific neuron groups forms our memories and experiences.
For years, experts believed that the brain learns by altering the connections between neurons: some synaptic pathways strengthen while others weaken based on new experiences. This process is known as synaptic plasticity.
Cracking the Code: Learning Rules Defined
To uncover the rules that guide synaptic changes during learning, researchers monitored individual synaptic activity in mice learning to perform a task for a reward. Surprisingly, they discovered that not all synapses on a neuron operate under the same learning principles.
While traditional theories posited that neurons follow Hebbian rules, where frequent firing leads to stronger connections, the study revealed a more complex picture. Different parts of the same neuron's dendrites adhered to varying rules, allowing for more nuanced adjustments.
The Implications: From Mental Health to AI
This revolutionary discovery allows for a deeper understanding of synaptic changes during learning and has significant implications for both mental health and technology. For example, conditions like depression may arise from weakened synaptic connections, leading to challenges in experiencing pleasure. Insights into synaptic plasticity could pave the way for better treatment options.
Moreover, these revelations could reshape artificial intelligence, where traditional models typically rely on uniform learning rules. By embracing the brain's multifaceted approach to learning, AI could become more efficient and capable.
What Lies Ahead?
While this research sets the stage for a better understanding of the brain's learning mechanisms, many questions remain unanswered. How do these differing rules function? What advantages do they confer to neuron activity?
As scientists continue to explore these mysteries, we inch closer to harnessing this knowledge for advancements in therapies for brain disorders and the future of artificial intelligence. Stay tuned for more discoveries in the ever-fascinating world of neuroscience!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)