
Unraveling the Mystery of Siberia's Bizarre Exploding Craters: The Startling Facts!
2024-10-03
Introduction
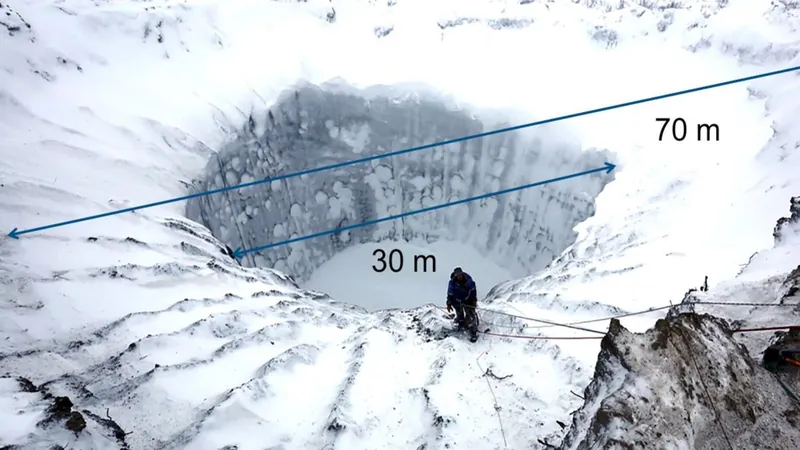
Scientists are inching closer to unraveling the enigma behind the colossal craters that have mysteriously appeared in Siberia's permafrost, sparking concern among climate scientists. These astonishing formations, measuring up to 230 feet (70 meters) wide and plunging 160 feet (50 meters) deep, are not merely geological oddities; they are manifestations of a potentially catastrophic phenomenon linked to climate change.
Discovery and Characteristics
First reported on Russia's Yamal and Gydan peninsulas in 2014, these craters display evidence of explosive eruptions, with debris from craters strewn across the landscape. Surprisingly, this phenomenon has not been observed elsewhere in similar Arctic climates, raising questions about the unique geological conditions of the region.
The Mechanism Behind the Explosions
According to researchers, the explosions occur when pressurized water infiltrates cracks in the permafrost, leading to the explosive release of methane gas. Ana Morgado, a chemical engineering doctoral student at the University of Cambridge and co-author of a new pivotal study, explained, "These are very, very specific conditions that allow for this phenomenon to happen. We're talking about a very niche geological space."
Implications for Climate Change
While these events may seem rare, their implications are dire. The release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, could trigger a vicious climate feedback loop, accelerating global warming. Morgado warns, "This might be a very infrequently occurring phenomenon, but the amount of methane that's being released could have quite a big impact on global warming."
The Role of Cryopegs
Over the last decade, various theories have attempted to explain the formation of these craters, linking them to the thawing of permafrost and the decomposition of methane hydrates—ice-like structures that contain methane. However, the newly published study in *Geophysical Research Letters* has shed light on the critical role of cryopegs, pockets of salty water beneath the surface. These unique formations—leftovers from ancient seas—remain liquid despite their frigid environment due to high pressures and salinity.
Process of Formation
As surface permafrost thaws due to rising temperatures, meltwater finds its way into these cryopegs, seeking to balance salt concentrations. This gradual process builds significant pressure within these pockets. Eventually, the strain can lead to cracks forming in the overlying permafrost, resulting in a rapid release of pressure. The methane hydrates lying below the cryopegs are destabilized by the sudden drop in pressure, leading to a dramatic and explosive release of methane gas.
Conclusion
As this process can take decades to unfold, the explosions producing these craters are infrequent but significant. Morgado likened their research to "detective work," piecing together the connections between these geological phenomena and their broader implications for climate science.
Call to Action
With climate change accelerating the thawing of permafrost globally, the discoveries in Siberia could be a harbinger of events elsewhere. Researchers are urging the global community to pay attention. The extraordinary craters may be just the tip of the iceberg in understanding how our warming planet could unleash even more unexpectedly dangerous greenhouse gases in the years to come.
Future Monitoring
Stay tuned as we continue to monitor the developments surrounding these explosive mysteries and their potential impacts on our climate future!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)