Unraveling the Secrets of the Marinoan Snowball: How Ice Ages Shaped Earth's Evolution
2025-04-23
Author: Jia
A Journey Through Earth's Icy Past
Earth has faced two major glaciation events known as the Sturtian and Marinoan snowball Earths during the Neoproterozoic Era, where vast expanses of ice covered the planet for millions of years. These periods were characterized by dramatic ice-albedo feedback loops that plunged the world into deep freezes, posing significant challenges to life.
The Mechanics Behind the Ice Ages
During these snowball climates, the process that typically consumes carbon dioxide (CO2) through silicate weathering stalls, leading to a buildup of CO2 in the atmosphere due to volcanic activity. Once enough greenhouse gases accumulate, they can trigger a thawing process, allowing Earth to recover from its icy grip.
The Mystery of Duration and Impact
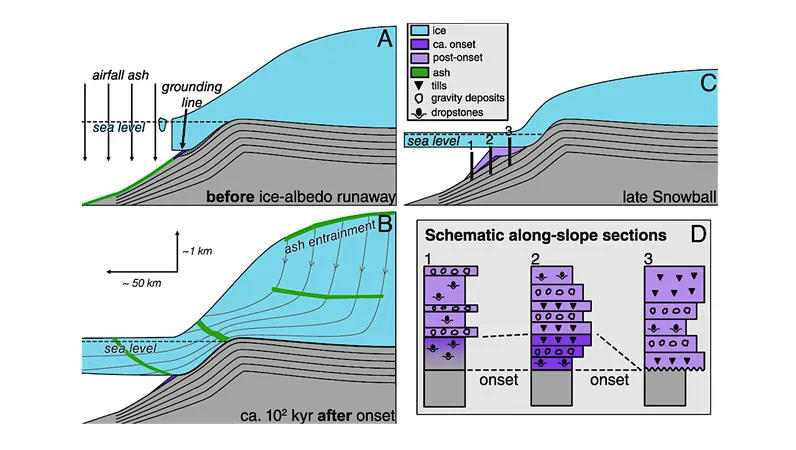
The extent and length of ice coverage are vital for determining how hospitable a planet can be, influencing whether life can not only survive but thrive. While scientists have confidently characterized the Sturtian glaciation at around 56 million years, the Marinoan glaciation has longer uncertain timeframes, ranging between 4 to 15 million years.
New Findings from Namibia
Recent research suggests that the Marinoan glaciation in Namibia lasted approximately 4 million years, with minimal vertical motion of less than 10 meters in ice grounding lines. This stability hints at the resilience inherent in a persistent snowball state, revealing how climatic conditions can be fragile yet stable at the same time.
Diverse Paths to Thawing
The striking difference in the lengths of these glacial periods illustrates that there were various routes to deglaciation. The prolonged Sturtian thawed slowly due to CO2 build-up, while the shorter Marinoan experienced a rapid change, likely driven by significant atmospheric changes.
Implications for Life on Earth and Beyond
Crucially, the brief Marinoan freeze might have been pivotal for the subsequent development and survival of early animal life on Earth. This highlights not just Earth’s history but also offers insights into potential habitability on exoplanets, emphasizing how different climatic scenarios can shape the trajectory of life.
Conclusion: Lessons from Earth's Ice Ages
As we delve into the mysteries of our planet's icy epochs, we gather valuable knowledge that can inform our understanding of life’s resilience in the face of extreme conditions, both on Earth and elsewhere in the universe.
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)