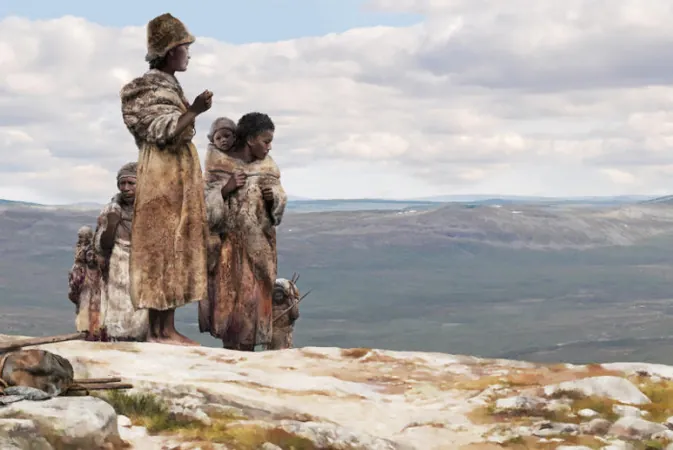

Unveiling Humanity's Journey: How a Small Group Shattered the Timeline of Human Migration from Africa
2024-12-16
Author: Yu
Introduction
About 45,000 years ago, a remarkable feat of resilience and adaptability unfolded as a minuscule band of fewer than 1,000 humans navigated the treacherous, icy landscapes of northern Europe. The frigid tundras were their hunting grounds, where they pursued colossal creatures such as the woolly rhinoceros. Interestingly, evidence suggests these Ice Age hunters had dark skin, possibly reflecting their African ancestry.
Survival and Adaptation
To survive the harsh cold, they fashioned clothing from the hides and furs of their prey, embodying the spirit of perseverance that characterized their existence. The group, referred to as the Lincombian-Ranisian-Jerzmanowician (LRJ) culture, left behind a legacy seen in their unique stone tools and skeletal remains scattered across various caves throughout Europe.
Genetic Discoveries
Recent advances in genetics have illuminated a fascinating chapter from our past, as researchers unveiled the genomes of seven individuals from the LRJ culture, making them the oldest known genetic specimens of modern humans ever discovered. These fossils, unearthed from sites in Germany and the Czech Republic, suggest that the LRJ were a part of a later wave of human migration from Africa, with their common ancestors diverging just 47,000 years ago—remarkably recent compared to other known migrations.
Challenging Long-held Beliefs
Contradicting long-held beliefs about the timeline of human expansion, this new evidence challenges the notion that modern humans had already reached continents like Australia and Asia as far back as 100,000 years ago. If the LRJ emerged just 47,000 years ago, it raises profound questions about the earlier human populations that roamed these vast lands and whether they left behind any genetic legacy.
Genetic Diversity and Community
As Johannes Krause, a noted geneticist from the Max Planck Institute, points out, earlier wave populations likely succumbed without contributing to current genetic diversity. The mystery deepens with the discovery that the LRJ peoples' genomes reveal striking genetic similarities, suggesting they existed as a small, closely-knit community with limited gene flow across vast distances.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The history of these ancient peoples is not merely academic; it highlights the struggles and adaptations of our ancestors amid severe climatic challenges. For decades, remnants of the LRJ culture stumped archaeologists, until recent excavations revealed connections between the skeletal remains found in the Czech Republic and Germany, including a mother and daughter pair.
Insights on Skin Color and Adaptation
Significantly, the absence of mutations linked to lighter skin tones in the LRJ population indicates their skin remained dark, akin to their African predecessors. This insight ties them intricately to the broader narrative of human adaptation and survival.
Migration Timeline and Neanderthal Interaction
These findings provide a clearer picture of human migration, signifying the split of Neanderthals from our ancestors approximately 600,000 years ago, their eventual extinction around 40,000 years ago, and the narrative of modern humans gradually spreading from Africa to other continents. Notably, the presence of Neanderthal DNA within LRJ genomes demonstrates a close interaction between these two hominin species.
Future Research Directions
Experts, including paleogeneticists Priya Moorjani and Pontus Skoglund, affirm that these revelations shed light on a previously compressed timeline of migration, indicating modern humans transitioned from the Middle East to Europe at an astonishing pace. Their insights also imply that earlier fossil dating may have required reevaluation, necessitating further exploration into ancient Asian specimens for clarity on this enigmatic chapter in human history.
Conclusion
As we continue to probe our roots, the unfolding discoveries of ancient genomes not only enhance our understanding of where we come from but also serve as a testament to human resilience in the face of adversity. Stay tuned for future revelations that will undoubtedly reshape the narrative of our ancestral journey!
Final Thoughts
Could this newfound understanding redefine our perspective on human evolution? The story is far from over!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)