Unveiling mRNA Export: The Secret Connection Between Cancer and Viral Infections!
2024-11-21
Author: Siti
Introduction
In the intricate tapestry of biology, the central dogma outlines the crucial flow of genetic information—transforming DNA into mRNA, which serves as the blueprint for protein synthesis. Vital to eukaryotic life, the export of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm is a fundamental process that drives cellular functioning.
Groundbreaking Study
A groundbreaking study recently published by Yi Ren, an assistant professor in Vanderbilt’s Department of Biochemistry, reveals a novel protein complex that significantly enhances our understanding of mRNA export mechanisms and their implications in herpes virus infections. This research, which appeared in the prestigious journal eLife, uncovers fascinating insights into how viruses manipulate these processes to propagate their infection.
Key Questions
Ren posed a pressing question: "With tens of thousands of mRNAs floating around in human cells, how does the cellular machinery adeptly manage and transport them from their birthplace in the nucleus to the cytoplasm where they influence protein synthesis?" This inquiry extends beyond theoretical curiosity; it underscores the intersection between fundamental biology and pressing health concerns.
Importance of mRNA Export
The significance of studying mRNA export is highlighted not only for our understanding of cellular functions but also for its critical relevance in infectious diseases. Numerous viruses, including influenza A, SARS-CoV-2—responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic—and now herpes viruses, hijack mRNA export pathways to silence host gene expression and elude immune responses, while promoting their own gene expression.
Global Impact of Viral Infections
The global impact of these viral infections is staggering. Influenza alone results in approximately a billion cases annually. Since its emergence, COVID-19 has led to around 200 million cases each year, while the herpes simplex virus type 1, linked to oral herpes, infects nearly half of the global population.
Details of the Research
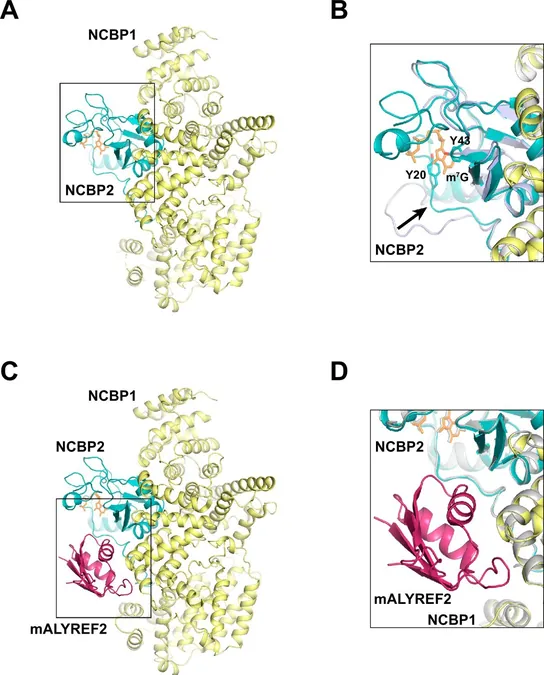
In the latest paper, lead author Bradley Clarke, alongside his research team, details the mRNA nuclear export pathway, highlighting crucial interactions that occur as newly synthesized mRNA is prepared for export. Utilizing advanced cryo-electron microscopy, Clarke elucidated the structure of the nuclear cap binding complex and a key mRNA export factor known as ALYREF.
Findings and Implications
Although the connection between these two components was established nearly twenty years ago by Robin Reed’s laboratory, the molecular details remained elusive—until now. Ren credits the dedicated team at the Cryo-EM Facility, which enables Vanderbilt researchers to access cutting-edge imaging technologies. The newly revealed structure provides molecular insights into how ALYREF facilitates the recruitment of mRNA export machinery to the 5' end of mRNA transcripts.
Impact on Cancer
The study also identifies a critical binding interface between CBC and ALYREF, suggesting that mutations at this site could lead to mRNA export dysregulation, which is significantly implicated in various cancers.
Viral Interactions
Interestingly, the research further indicates that herpes viruses, particularly KSHV (associated with Kaposi's sarcoma) and HSV-1, target this crucial CBC-ALYREF interaction. Ren's team posits that these viruses likely inhibit mRNA export by interfering with this interaction, thereby disrupting host gene expression.
Future Directions
Moving forward, Ren's laboratory aims to uncover how ALYREF orchestrates the various stages of mRNA nuclear export and whether these processes are conserved across evolutionary lines. Their findings could reveal novel therapeutic targets for antiviral treatments and enhance our understanding of how mRNA export malfunctions contribute to cancer development.
Conclusion
As the fight against viral infections and cancer continues, this cutting-edge research invites scientists and medical professionals alike to consider the hidden connections between cellular machinery and disease, paving the way for innovative treatment strategies in the future!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)