Unveiling the Alarming Rise of Depression during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Global Call to Action!
2024-12-23
Author: Wei
The COVID-19 pandemic has not only caused widespread health and economic turmoil but has also vastly impacted mental health around the world. Recent studies highlight a staggering increase in depression rates among various populations as mental wellness has plummeted during this unprecedented crisis. Here’s an overview of the findings shedding light on the global mental health landscape during and after the pandemic.
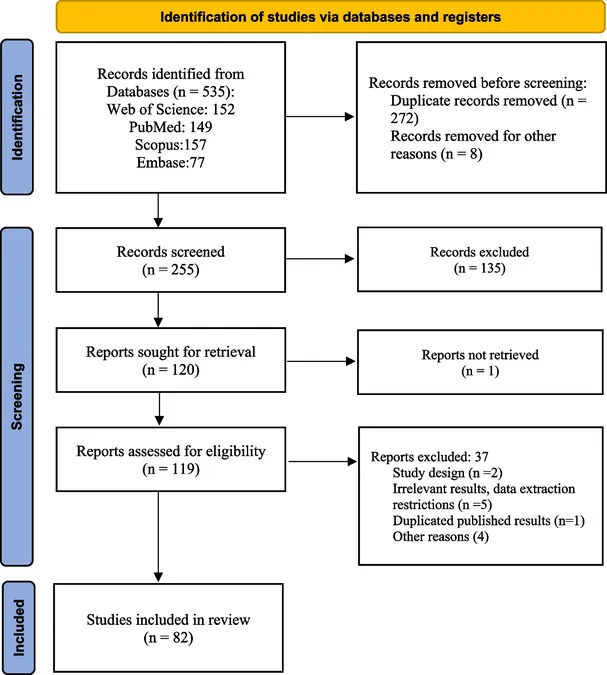
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the pandemic triggered a staggering 25% rise in anxiety and depression worldwide. Specifically, a systematic review and meta-analysis conducted during this time revealed critical insights into the prevalence of depressive symptoms not only among healthcare workers but also spanning diverse demographics, including children, adolescents, pregnant women, and individuals from varying socioeconomic backgrounds.
Healthcare professionals, bearing the brunt of patient care during the pandemic, reported alarming levels of anxiety and depression. Studies from different regions have estimated that up to 50% of healthcare workers experienced significant depressive symptoms. This exposure is compounded by heightened stressors, including long hours, a shortage of personal protective equipment, and the emotional toll of dealing with severe illness and death on a daily basis.
Children and adolescents have not been spared either, with reports indicating that rates of depression in these age groups surged due to social isolation, the disruption of routines, and the uncertainties surrounding school closures. A recent meta-analysis revealed that students displayed increased levels of depressive symptoms during lockdowns, raising concerns about their long-term mental health and wellbeing.
Moreover, pregnant women faced unprecedented levels of anxiety and stress, leading to increased rates of postpartum depression. The interplay between economic strain, disrupted social networks, and fear of infection has created a perfect storm for mental health challenges. Research shows that these women require targeted mental health interventions to support their wellbeing during and after their pregnancies.
As countries begin to navigate the post-pandemic landscape, the mental health crisis stemming from COVID-19 demands urgent attention and systematic planning. Experts are calling for integrated mental health services into primary healthcare systems to address the growing need for support and treatment across affected populations.
It's crucial for governments, organizations, and communities to recognize the long-term implications of mental health deterioration and take decisive action. Increasing funding for mental health initiatives, promoting awareness, and simplifying access to mental health resources are imperative steps that can facilitate recovery and resilience in the aftermath of this global crisis.
In conclusion, the COVID-19 pandemic has sparked an unprecedented mental health crisis that endangers not just the immediate wellbeing of affected individuals but poses broader implications for societal health. With a unified global response, we can work towards healing and ensuring that mental health does not remain a forgotten sector as we emerge from this crisis.
Stay tuned as more studies and recommendations will continue to illuminate the path toward recovery in mental health as we grapple with the aftermath of COVID-19!





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)