Unveiling the Hidden Truths Behind Benign Skin Tumors in the Elderly: A Groundbreaking Study
2025-04-05
Author: Jia
Key Findings on Risk Factors and Prevalence
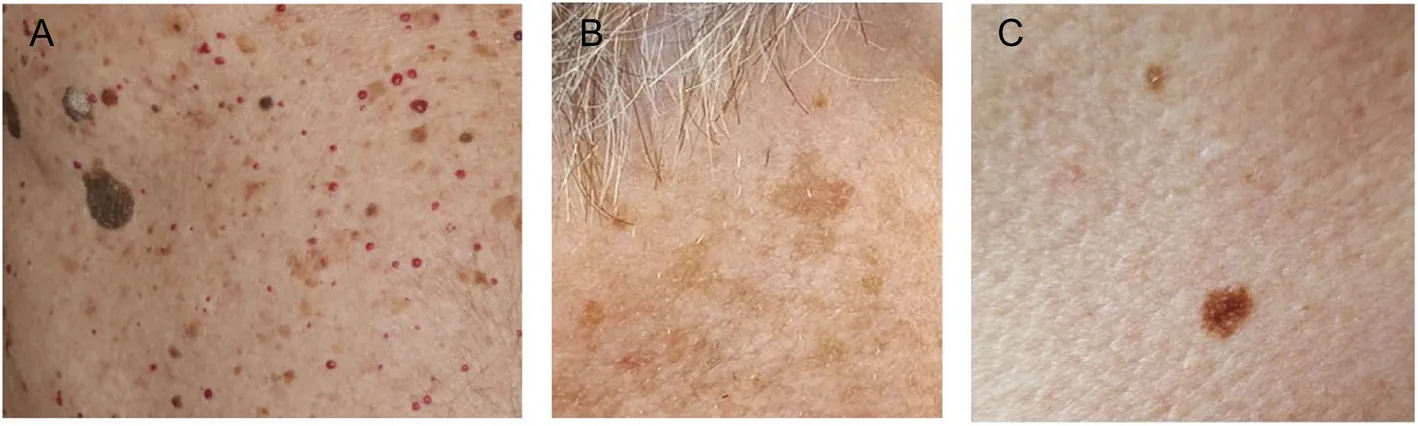
Seborrheic keratosis emerged as the most common benign tumor, affecting more men than women (21.6% vs. 12.1%). The prevalence of these tumors was notably higher among those with a history of outdoor work and those with darker skin types. Interestingly, the data hinted at associations with lifestyle factors such as smoking, where multiple instances of seborrheic keratosis were more common among smokers.
Lentigo solaris, often associated with age and sun exposure, was significantly more frequent in older women. The data suggested that outdoor working history also played a role, although the statistical significance was not robust. Similarly, multiple cherry angiomas were found predominantly in females and were linked to metabolic factors, particularly lower levels of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), suggesting a possible connection between skin health and metabolic conditions.
The Unexplained Rise: What's Driving the Increase?
Interestingly, while the study aligned with previous research indicating a rise in benign tumors with age, it raises questions about the exact mechanisms behind this trend. Despite the clarity surrounding the association with sun exposure and outdoor jobs, the exact reasons for the frequent emergence of these tumors in the elderly remain largely unexplained.
Previous studies, including a substantial Iranian survey, reported that benign skin neoplasms were present in more than two-thirds of their subjects over 60, supporting the global relevance of this issue. In Germany, over half of older participants reported similar findings regarding seborrheic keratosis.
Research Implications: More Than Just Skin Deep
As striking as the prevalence rates are the implications for healthcare systems coping with the aging population. Benign skin tumors, while not malignant, can complicate diagnosis and become a significant source of distress among patients. Misidentifying these benign tumors as malignant can lead to unnecessary stress and healthcare costs, emphasizing the importance of educating both patients and healthcare providers on the nature and management of these skin conditions.
Moreover, the potential links between lifestyle factors such as smoking and family planning indicate the necessity for further research to unravel the connections between benign tumors and various lifestyle parameters. Notably, the study suggests that women with multiple cherry angiomas reported having fewer children, adding a new layer of complexity to the understanding of benign tumor development.
The Path Forward: Rethinking Prevention Strategies
In conclusion, the findings of this significant study underscore the growing importance of benign skin tumors in elderly populations. With an increasing number of individuals reaching advanced ages, distinguishing between benign and potentially malignant changes becomes crucial. Dermatological evaluations by skilled professionals can reduce misdiagnosis and enhance patient care.
As researchers continue to probe the depths of these findings, the quest for effective prevention strategies and a deeper understanding of the etiology of benign skin tumors may lead to improved healthcare strategies for aging populations. It's time for both healthcare providers and the public to take benign skin tumors seriously and understand their implications on overall health and well-being.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)