Are We on the Brink of a Human Bird Flu Pandemic? Here’s What You Need to Know!
2025-03-31
Author: Jacob
Are We on the Brink of a Human Bird Flu Pandemic? Here’s What You Need to Know!
As our world faces a multitude of emerging health threats, experts are sounding the alarm about a potential shift in the bird flu virus, H5N1, which might be gearing up for human transmission. This situation is alarming—out of over 900 known global cases of H5N1 since 2003, nearly half have resulted in fatalities. This staggering mortality rate is 20 times greater than that of the infamous 1918 flu pandemic, which should make us take this threat very seriously.
Recent studies highlight the steady evolution of H5N1, reflecting a broader pattern of zoonotic diseases—those that can jump from animals to humans. The pattern of infection raises a red flag: if H5N1 successfully adapts to human transmission, we could find ourselves in the midst of a global health catastrophe.
Understanding Spillover: A Treacherous Journey for Viruses
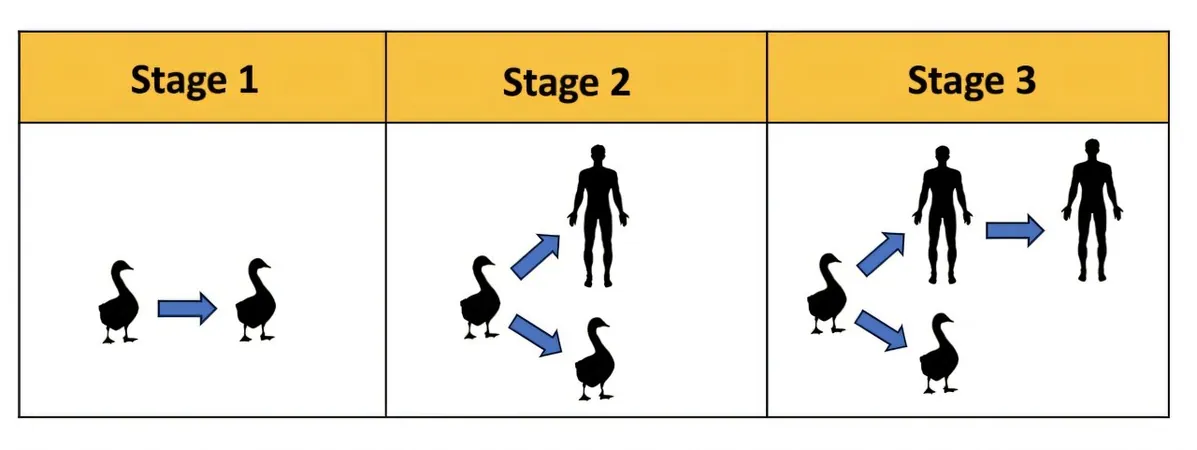
The process known as "spillover" is critical to understanding how H5N1 could transition from birds and other animals to humans. For a virus to jump species, it must find the right "keys"—molecular structures that allow it to access host cells. Given that these structures can differ vastly between species, the virus typically faces multiple hurdles and needs a series of genetic mutations to succeed.
Additionally, the pathway is fraught with complications. While human infections may occur sporadically, they often only happen in individuals who have been in close contact with infected animals. This has been true for several recent outbreaks clustered around poultry and dairy workers, suggesting that while human cases are alarming, they may not imply widespread transmission just yet.
Epidemiologists refer to this phenomenon as "viral chatter," a series of isolated infections that act like disjointed signals warning of a potential outbreak. Each case may be just a whisper today, but the underlying message remains ominous—a future human pandemic could be on the horizon.
The Rapid Evolution of Influenza: A Race Against Time
Influenza viruses are notorious for their rapid evolution. Factors like co-infections with multiple virus strains can lead to genetic reshuffling, encouraging new viral variants that may possess the critical traits for effective human-to-human transmission. With H5N1 already having infected over 450 animal species, the danger of widespread outbreaks grows daily.
Taking Action: Strategies to Slow the Threat
The silver lining in this dire situation is that preventative measures can be taken. We have the tools and knowledge to potentially mitigate the threat posed by H5N1.
1. Responsible Animal Care: Improving the management of food animals is essential. By addressing unsanitary conditions in large-scale poultry farming and reducing the geographic transfer of live poultry, governments can minimize the factors that facilitate viral evolution and intermingling.
2. Vaccination Awareness: Individuals should prioritize vaccination against seasonal influenza. While this may not seem directly connected to H5N1, reducing the prevalence of common flu viruses will limit opportunities for avian strains to mutate into a form capable of sustained human transmission.
3. Strengthening Population Health: On a larger scale, bolstering nutrition and sanitation in underserved communities can drastically improve resilience against new infections. Health issues in one community can swiftly ripple across the globe, highlighting the interconnectedness of our societies in facing disease threats.
In conclusion, for over 10,000 years, human behaviors have influenced the evolution of infectious diseases. By collectively reshaping these behaviors, we can steer the trajectory of health crises towards a safer future. As scientists continue to monitor the situation, the message is clear: it’s time to act before it’s too late!









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)