Breakthrough AI Mammography Platform Aims to Revolutionize Early Breast Cancer Detection
2024-10-03
Introduction
In an exciting advancement for women's health, a large retrospective study highlights the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) to detect high-risk cases of breast cancer up to six years before traditional methods might flag them. This groundbreaking study, published in JAMA Network Open, focuses on the AI mammography system known as Insight MMG (version 1.1.7.2, Lunit), which analyzes mammogram images to gauge the probability of developing breast cancer on a scale from 0 to 100.
Study Details
The research involved analyzing three rounds of biennial mammography screening for women with no prior history of breast cancer. The findings were striking: during the first screening round, the average AI score for women who later developed screening-detected cancer (SDC) was 19.2, significantly higher than the 9.5 score for those who did not develop cancer. This pattern of increasing AI scores continued to grow in subsequent screenings, with scores rising to 30.8 vs. 8.2 in the second round and a dramatic 82.7 vs. 5 in the third.
Interval Cancers
The results also revealed significant insights into interval cancers—those that are diagnosed between scheduled mammograms. In the initial screening, breasts developing interval cancer had a mean AI score of 17.8, compared to only 10.1 in contralateral breasts not developing any cancer. The disparity widened in later screenings, emphasizing the AI system's capacity to identify risks that may go unnoticed through conventional evaluation.
Expert Insight
Dr. Solveig Hofvind, the study's co-author and leading expert in mammography, reflected on the implications: "While commercial AI tools have not been specifically designed for predicting future cancer risk, our findings demonstrate that their accuracy can surpass traditional risk calculators, establishing a new paradigm in breast cancer screenings."
Performance Metrics
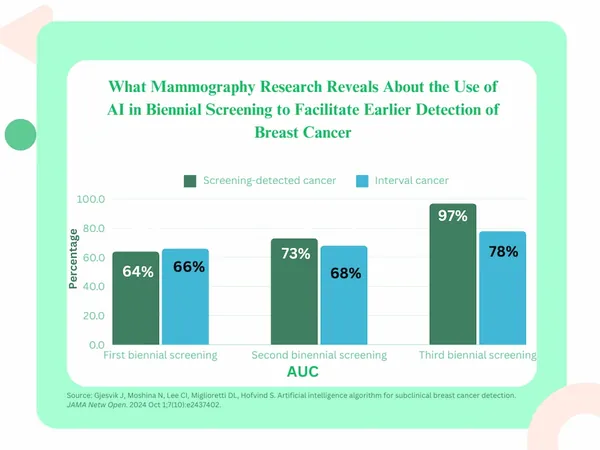
The AI’s performance metrics were impressive, achieving an area under the curve (AUC)—a measure of prediction accuracy—of 64% in the first round of screenings, which improved substantially to 97% by the third round for distinguishing between patients with and without cancer. This surpasses the efficacy of established risk calculators like the Tyrer-Cuzick model and the Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool (BCRAT), which have AUCs ranging between 56% and 71%.
Implications for Healthcare
Experts believe that such AI applications could lead to streamlined mammography interpretations, informing radiologists of individual risk factors, even when those details are not available through standard protocols. This can ultimately lead to more efficient and personalized screening strategies, enabling healthcare providers to address women’s unique risk profiles effectively.
Key Takeaways
1. **AI's Foresight:** The Insight MMG AI Mammography platform has demonstrated its ability to identify women at high risk of breast cancer years in advance, showcasing an increase in accuracy over multiple screenings.
2. **Superior Performance:** When benchmarked against traditional cancer risk calculators, the AI's predictive accuracy significantly outperformed them, especially noted by the third screening session.
3. **Urgency in Screening:** The study indicated a concerning trend that interval cancers might develop faster than SDCs, highlighting the critical need for improved detection methodologies in early-stage screenings.
Conclusion
Overall, while the results of this study are promising, the authors acknowledged limitations, including the retrospective nature of the trial and the lack of racial diversity in participants, which could influence the applicability of the findings. As AI technology continues to evolve, the future of breast cancer detection looks poised for transformation, potentially saving countless lives by catching cancers earlier than ever.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)