Breakthrough Research Uncovers Key Mechanism Behind Axon Guidance in Neural Development
2024-12-16
Author: William
Groundbreaking Discovery in Neuroscience
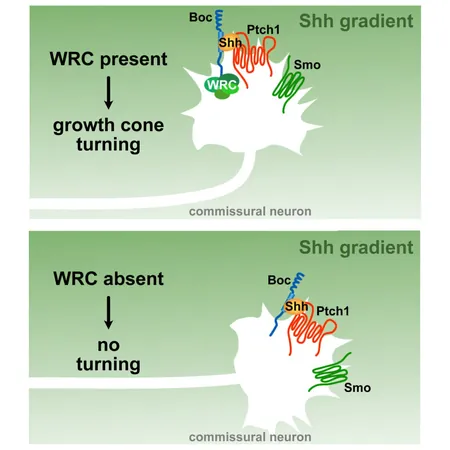
An international research team led by Professor Frédéric Charron from Université de Montréal has made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of neuroscience, revealing a crucial interaction between the WAVE complex and the Boc receptor that plays a pivotal role in guiding developing axons. This pioneering study, published in iScience in November, sheds light on the complex mechanisms behind neuronal development, potentially paving the way for new therapeutic strategies for neurological disorders.
The Importance of Axon Guidance
Axon guidance is a vital process during which axons—the elongated part of neurons responsible for transmitting nerve impulses—navigate towards their intended targets. This journey relies heavily on the actin cytoskeleton, a skeletal-like network of proteins within cells that provides structure and support, much like the human skeleton.
Key Interactions Revealed
Charron's research highlights that the WAVE complex, previously recognized for its role in assembling the actin cytoskeleton, has a direct interaction with the Boc receptor, which is essential for signaling initiated by the guidance molecule Sonic hedgehog (Shh). This interaction is critical for ensuring that developing axons are accurately guided to their destinations.
The Role of Sonic Hedgehog
Sonic hedgehog serves as a significant attraction signal during embryonic development. Charron and his team had established in previous studies that the Boc receptor mediates the attraction of axons via Shh. However, the precise molecular mechanisms behind this process remained elusive until now. The recent findings pinpoint the WAVE complex as a key facilitator in the cytoskeletal changes necessary for effective axon guidance.
Implications for Neurological Disorders
Understanding these intricate molecular interactions is not just an academic exercise; it has profound implications for addressing neurological disorders. Defects in axon guidance can lead to serious complications in nervous system development and are implicated in various neurological diseases, such as autism spectrum disorders and schizophrenia.









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)