Groundbreaking Breakthrough: Discovering the Structure of a Hybrid Catalyst that Transforms Sunlight into Hydrogen Fuel!
2024-12-12
Author: William
Groundbreaking Breakthrough: Discovering the Structure of a Hybrid Catalyst that Transforms Sunlight into Hydrogen Fuel!
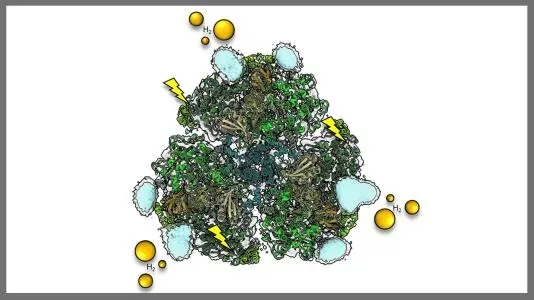
In an extraordinary advancement for clean energy production, researchers from Argonne National Laboratory and Yale University have unveiled the complex structure of a novel photosynthetic hybrid catalyst. This groundbreaking work, which focuses on utilizing the photosystem I (PSI) protein in conjunction with platinum nanoparticles, marks a significant step forward in the quest for sustainable hydrogen fuel.
Unlocking the Secrets of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is one of nature's most efficient methods for converting sunlight into chemical energy, essential for life on Earth. Within this remarkable process, photosystems play a pivotal role, serving as the engines that convert light energy into usable chemical energy. By combining PSI with tiny platinum nanoparticles capable of catalyzing hydrogen production, scientists have created a biohybrid catalyst that harnesses sunlight to generate this clean energy source.
A Decade of Dedication
“It’s incredibly thrilling to finally observe the system we’ve dedicated 13 years of work to,” stated Lisa Utschig, a chemist at Argonne. The recent research breakthrough involves a high-resolution visualization of the PSI biohybrid catalyst, accomplished using cutting-edge cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). This achievement not only highlights the structure of the biohybrid but also paves the way for the development of advanced solar fuel systems, offering a potentially sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
The Role of PSI in Energy Conversion
PSI, a large protein complex found in plants, algae, and photosynthetic bacteria, is remarkable in its ability to convert sunlight into energy efficiently. For every photon absorbed, it typically generates one electron, which can then be transferred to the platinum nanoparticles to produce hydrogen gas.
Unexpected Discoveries
Despite previous investigations into the properties of PSI biohybrids, researchers have struggled to pinpoint the exact attachment sites of the platinum nanoparticles. However, Utschig and her team’s new findings reveal that the nanoparticles bind at two unexpected locations on the PSI protein. “We initially thought the nanoparticles were connecting at the electron transfer partners, so discovering these two distinct sites was a real surprise,” Utschig explained.
Optimizing Energy Production
Armed with this structural knowledge, scientists can further optimize the interaction between PSI and the nanoparticles to enhance catalytic efficiency. This innovation can lead to biohybrids specifically engineered for improved performance by tweaking both the protein properties and the makeup of the nanoparticles.
Significance of the Research
Utschig elaborated on the significance of this research, stating, “It's fascinating to observe bioenergy at the molecular level and to witness the collaboration between a synthetic particle and a natural protein to produce energy.”
Collaborative Research Efforts
The collaborative effort behind this remarkable research also included contributions from a team of esteemed researchers, ensuring a multi-faceted approach to this groundbreaking work.
Funding and Future Prospects
The results, published in the influential journal Nature Communications, underscore the importance of federal support in advancing scientific exploration—particularly through funding from the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Basic Energy Sciences and the National Institutes of Health.
The Promise of Renewable Energy
As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy sources and hydrogen technology, this discovery represents a pivotal moment in the ongoing search for cleaner, more sustainable fuel solutions. The potential impact of this research could drive significant advancements in the hydrogen market and beyond. The future is indeed bright for the integration of green technology and sustainable energy production—stay tuned for more incredible updates on this frontier!









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)