Groundbreaking Model Promises Significant Reduction in Methane Emissions from Rice Paddies!
2024-12-02
Author: Liam
Introduction
Rice paddies are surprisingly one of the largest contributors to global warming, accounting for nearly 10% of global anthropogenic methane (CH₄) emissions. With climate change becoming an ever-pressing issue, reducing these emissions from rice cultivation is critical to meeting international climate targets, particularly in efforts to achieve carbon neutrality and peak emissions reduction.
Research Team and CH4MOD
A pioneering research team from China, led by the esteemed Prof. Li Tingting from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has made remarkable progress in this arena. They have successfully validated an innovative methane emission model known as CH4MOD, which operates on a global scale. This groundbreaking research underscores the distinct advantages of process-based models over the traditional emission factor method commonly used in environmental studies.
Advantages of CH4MOD
While the emission factor method relies on broad, generalized estimates that can often ignore essential variables such as environmental conditions and management practices, CH4MOD takes a much more nuanced approach. This sophisticated model meticulously simulates not just methane production and oxidation, but also emissions, considering critical elements like climate variation, soil characteristics, organic matter content, and water management techniques.
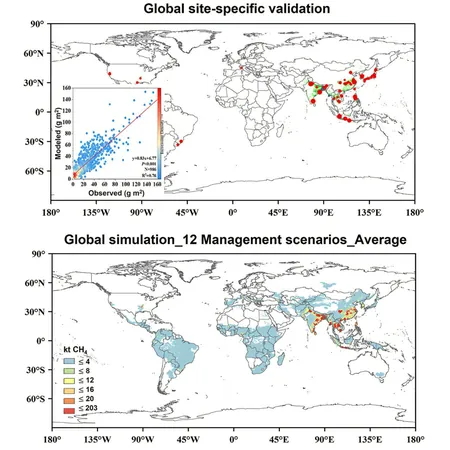
Validation of CH4MOD
Published in the peer-reviewed journal *iScience*, the study utilized a vast dataset of 986 methane flux observations from across the globe to validate CH4MOD. The results were compelling, with the model displaying a strong correlation coefficient of 0.76 and a model efficiency of 0.78 when compared to real-world data. Such findings powerful validate CH4MOD's ability to accurately simulate methane emissions from rice paddies under a wide variety of environmental conditions and agricultural practices.
Significance and Future Implications
Prof. Li emphasized the significance of these results, stating, "Our findings demonstrate how mechanistic models like CH4MOD can reduce uncertainties in methane emission inventories and enable more effective mitigation strategies." This advancement in modeling may lead to targeted interventions in rice cultivation, ultimately playing a critical role in combating climate change.
Conclusion
As countries worldwide strive to adopt sustainable agricultural practices and meet their carbon footprint reduction commitments, innovations like CH4MOD could prove invaluable. With its enhanced predictive capabilities, the model offers a glimmer of hope and a pathway towards more effective management of methane emissions, potentially transforming the future of rice production and its environmental impact. Stay tuned as the global community rallies to implement these groundbreaking strategies in rice cultivation to protect our planet!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)