
Groundbreaking Research Unveils Eco-Friendly Polymers that Detect Toxic Gases in Extreme Conditions!
2024-11-25
Author: Olivia
Introduction
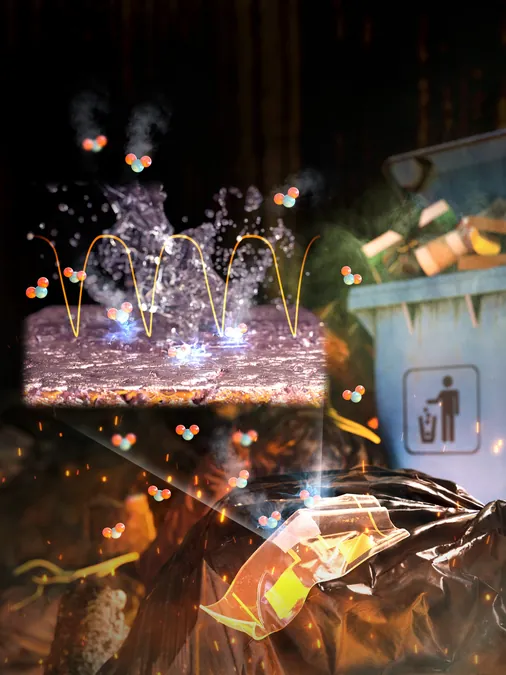
In a significant breakthrough for the field of wearable electronics and environmental monitoring, researchers from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have developed a novel method for synthesizing polymeric nanomaterials that can detect harmful gases in extreme conditions. Traditionally, while polymers have been favored for their lightweight and flexible properties, their low electrical conductivity and reliance on toxic solvents have hindered their potential in practical applications.
Innovative Approach
Collaborating with Dr. Jang Ji-soo of KIST and Professor Mingjiang Zhong of Yale University, this research overcomes these limitations by introducing ionic pendant groups into the polymer structure. This innovative approach allows for the use of eco-friendly solvents, specifically 2-methylanisole, enabling the creation of conjugated polymers that not only dissolve in sustainable materials but also exhibit impressive electrical conductivity.
Key Findings
The findings, published in the esteemed journal Advanced Functional Materials, highlight the polymer's high gas sensing performance, particularly in challenging environments characterized by elevated temperatures and humidity levels. Remarkably, the n-type conductive polymer known as N-PBTBDTT demonstrated an astounding sensitivity of 189% for nitrogen dioxide (NO2) detection, even at concentrations as low as 2 parts per billion (ppb).
Applications
This sensitivity and durability surpass traditional sensor technologies, making it a promising candidate for applications in various fields such as wearable technology, portable electronics, and industrial sensors. The polymer's ability to maintain stable performance even at humidity levels of 80% and temperatures reaching 200°C aligns with the increasing demand for reliable sensors in demanding environments.
Expert Insights
Dr. Jang Ji-soo expressed optimism regarding the impact of this research, stating, "The sensors developed in this research go beyond simple chemical sensors and can bring about revolutionary changes in various applications." This advancement not only promises enhanced safety through effective gas detection but also paves the way for sustainable technology development without compromising performance.
Conclusion
The potential to integrate these eco-friendly polymers into everyday devices marks a turning point in the quest for safer, smarter, and environmentally sustainable technologies. As research continues to evolve, the implications of these findings could dramatically change how we approach pollution monitoring and environmental health on a global scale.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)