
Historic Glacial Outburst in Greenland Could Foreshadow Climate Change Catastrophes
2024-12-16
Author: Jacques
Introduction
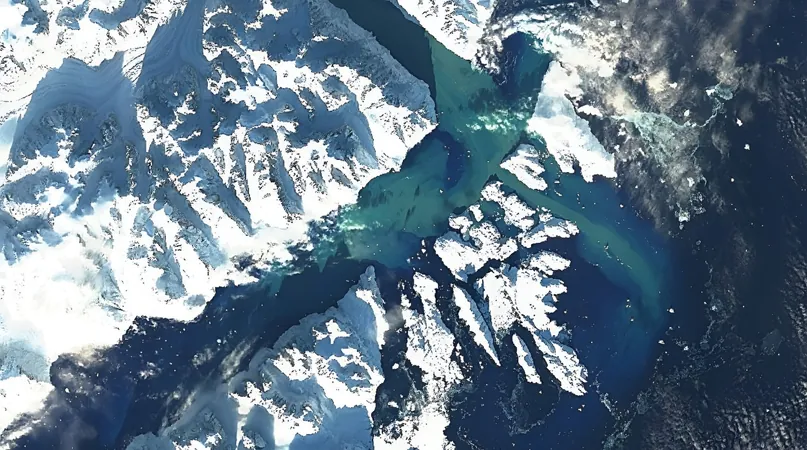
For the first time ever, scientists have successfully witnessed a monumental glacial lake outburst in East Greenland, with immense implications for our understanding of climate impacts. Researchers from the University of Copenhagen observed this staggering event in real-time, which involved an astonishing release of over 3,000 billion liters of meltwater – that's three times the total annual water consumption of Denmark – all within a matter of weeks.
What is a Glacial Outburst?
Now, you might be wondering: What exactly is a glacial outburst? Also known as a glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF), this phenomenon occurs when a glacial lake suddenly releases a massive volume of water. Such lakes often form behind ice or debris dams as meltwater accumulates. Over time, the pressure becomes too great, leading to a catastrophic failure of the dam and unleashing torrents of water that can result in severe flooding, erosion, and even devastation of infrastructure and communities downstream.
The Event at Catalina Lake
In this case, the event originated from Catalina Lake in East Greenland. The lake, long held back by the gargantuan Edward Bailey Glacier, unleashed approximately 3.4 cubic kilometers (about 0.8 cubic miles) of water into Scoresby Sound fjord. Between September 23 and October 11, the lake's water level plummeted by a dramatic 154 meters. This event not only ranks among the largest glacial outbursts on record but also marked the first occasion researchers were able to monitor and measure such an occurrence live using satellite technology.
Significance of the Findings
Aslak Grinsted, a climate researcher from the Niels Bohr Institute, highlighted the breakthrough nature of these observations, saying, “We’ve previously found traces of similar outburst floods, but the combination of polar night and cloud cover had hindered our ability to monitor them in real time.” Catalina Lake had been quietly accumulating meltwater for over two decades, carving a 25-kilometer (15.5 miles) tunnel beneath the glacier, which ultimately became the route through which the water escaped.
Implications of Global Warming
A crucial takeaway from this event is that the danger passed by glacier-dammed lakes is escalating due to global warming. Grinsted stressed the need for improved understanding of these phenomena to provide timely warnings for potentially impacted communities. While the sparse population in Greenland meant that this outburst resulted in no harm, the gravitas of the situation is magnified when considering more populous regions around the globe.
Global Threat of GLOFs
For instance, catastrophic glacial floods have already wreaked havoc in mountainous areas, such as the Himalayas, where entire villages have been obliterated and lives lost. A 2023 study indicates that up to 15 million people around the world currently live under the threat of deadly GLOFs. Grinsted cautions, “I expect to see even larger outbursts from these ice-dammed lakes as Greenland's ice sheet continues to melt in the coming centuries.”
Energy Potential of Meltwater Outbursts
Interestingly, the energy released during the recent glacial flood equaled the operating output of the world’s largest nuclear power plant running at full capacity for 22 days. The sheer magnitude of this energy, which could potentially power a small town continuously at 50 megawatts, raises questions about sustainable harnessing; however, the remote locations of such events complicate logistics.
Conclusion
The nearest settlement to the recent outburst is a staggering 180 kilometers away, with just 350 residents. “Infrastructure is a critical issue here in Greenland. Yet, if we can find innovative ways to tap into the energy of these meltwater outbursts, there is substantial potential waiting to be harnessed,” Grinsted concluded.
The dramatic glacial outburst is a stark reminder of the alarming risks posed by climate change. Continued research into glacial dynamics is imperative, not just for providing effective early warnings, but also for potentially transforming these natural phenomena into valuable energy resources. The fight against climate change continues, and understanding the raw forces of nature may be key to our survival in the future.







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)