
Hubble's Stunning Discovery: The Mystery of NGC 4694 - A Galaxy Like No Other!
2024-11-24
Author: Sophie
Introduction
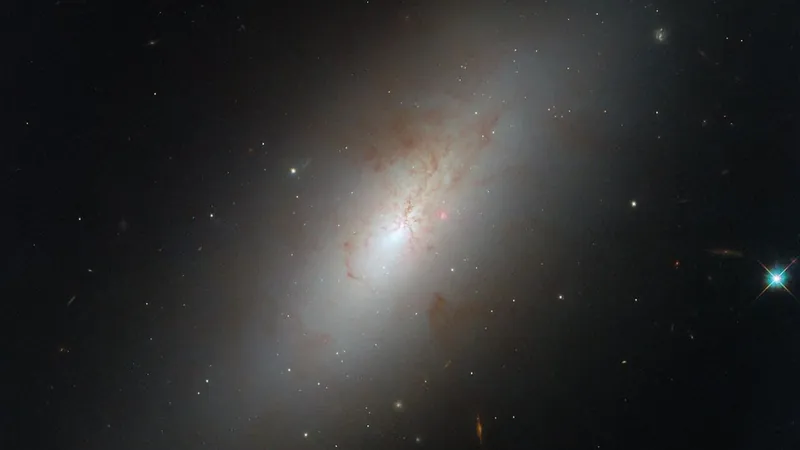
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has unveiled the extraordinary nature of NGC 4694, a unique galaxy situated 54 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. Unlike traditional galaxies, NGC 4694 defies easy classification, exhibiting features of both spiral and elliptical galaxies that have left astronomers intrigued.
Spiral vs. Elliptical Galaxies
Spiral galaxies, like our very own Milky Way, are vibrant and rich in star-forming gas, presenting beautiful spiral arms filled with young, bright stars. On the other hand, elliptical galaxies are more serene, typically composed of older, redder stars, and lack the dynamism found in their spiral counterparts. Most galaxies fall into these well-defined categories, but NGC 4694 blurs the lines between them.
Hubble's Findings
Hubble's team reported that while NGC 4694 presents a smooth, featureless profile reminiscent of elliptical galaxies, it also boasts a central region bustling with relatively young stars. Such star formation aligns more closely with spiral characteristics, making the classification puzzle even more complex. The galaxy is abundant in hydrogen gas and dust, vital ingredients for creating new stars, which contrasts sharply with traditional elliptical galaxies that tend to lack this essential material.
Peculiar Features and Cosmic Interaction
A closer examination reveals peculiar reddish-brown dust structures radiating from NGC 4694’s core, as well as a fascinating bridge of hydrogen gas leading to a smaller nearby galaxy, VCC 2062. This connection suggests that these two galaxies may have experienced an intense interaction—likely a collision—enabling the larger NGC 4694 to siphon gas from its diminutive neighbor. This dramatic event has contributed to its distinctive armless and smooth structure with an active star formation center, ultimately classifying it as a lenticular galaxy.
Understanding Lenticular Galaxies
Lenticular galaxies serve as a bridge between the elliptical and spiral designs. They possess a prominent central bulge and a broad disk but lack the exuberant spiral arms typical of spiral galaxies. Interestingly, they also harbor more star-forming resources than standard elliptical galaxies, allowing for new star creation.
Conclusion
This breathtaking image, captured by combining ultraviolet and optical data through Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3, serves as a testament to the continual revelations of the universe. With every discovery made by Hubble, we gain further insight into the complexities and beauty of the cosmos that surrounds us.
What’s Next?
Get ready—there's more cosmic magic to be unleashed! Astronomers are on the lookout for rare formations and characteristics in galaxies that challenge our understanding of cosmic evolution. Stay tuned for the next astronomical revelation that could change the way we perceive the universe!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)