Revolutionary MS Drug Shows Promise in Heart Attack Recovery, Sparking Hope for Millions
2024-12-26
Author: Olivia
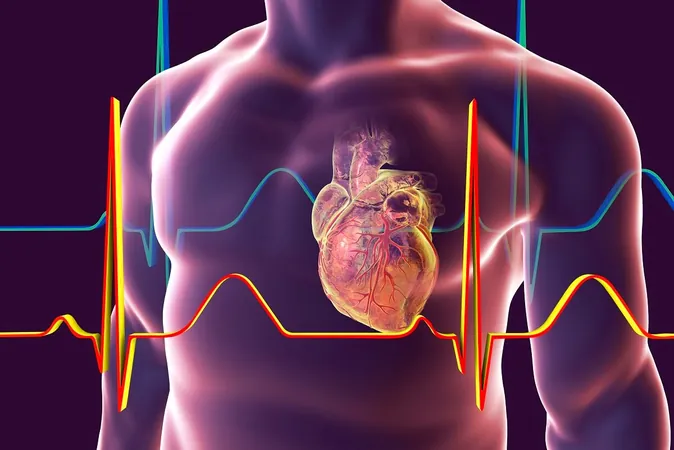
In an exciting medical breakthrough, researchers have found that Copaxone, a well-known medication traditionally used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS), is making waves in the field of cardiology. This innovative drug has demonstrated remarkable potential in protecting and regenerating heart muscle after a heart attack, marking a significant advancement in post-attack recovery.
Published on December 26, 2024, recent studies indicate that Copaxone not only reduces damage to the heart muscle but also enhances overall cardiac function. This dual action could represent a game-changer for patients recovering from myocardial infarctions, bringing hope to those at risk of cardiac complications.
The mechanism behind Copaxone's protective qualities lies in its ability to modulate the immune response, which is a critical factor in the healing process following a heart attack. By reducing inflammation in the heart, the drug helps to limit further damage to heart tissue, allowing for better recovery and regeneration of the affected areas.
Moreover, experts are optimistic that the application of Copaxone in this new capacity could open doors to novel treatments aimed at improving heart health. For many individuals living with heart disease, the prospect of using an established drug that has already passed through safety evaluations offers renewed hope and could simplify the path towards recovery.
This revelation comes at a time when heart disease remains a leading cause of mortality worldwide, affecting millions. With ongoing research and clinical trials, the medical community is keenly watching the developments surrounding Copaxone’s potential cardiovascular applications. Could this drug redefine post-heart attack care and drastically improve survival rates? Only time will tell, but for now, the future looks promising.
Stay informed as we continue to uncover the latest advancements in heart health and the extraordinary potential of repurposed medications!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)