Shocking Truth: High Rates of Undiagnosed ADHD Among Medical Students in Pakistan Revealed!
2024-11-25
Author: Emily
Introduction
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a prevalent neurodevelopmental disorder that has long been misunderstood. Characterized by difficulties in maintaining attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, ADHD can severely impact various aspects of life, from academic performance to mental health. While often thought to only affect children, recent studies reveal that ADHD symptoms continue into adulthood—a reality that often goes unrecognized in adults, including medical students who are poised to be future healthcare providers.
Survey Findings
A new survey, spanning from July to December 2023, has shed light on the alarming rates of undiagnosed ADHD among undergraduate medical students in Pakistan. Approximately 34.8% of medical students surveyed exhibited symptoms consistent with adult ADHD, a significant finding given that earlier studies globally reported prevalence rates between 5.5% to 23.7% for medical students. The new revelation from Pakistan indicates a worrying trend that is likely to strain both personal well-being and professional competency.
Research Methodology
The survey utilized a cross-sectional web-based format, capturing responses from medical students across Pakistan's four provinces—Sindh, Punjab, Balochistan, and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. What sets this research apart is its focus on not just prevalence, but also the students' knowledge and perceptions of ADHD. Surprisingly, 82.5% of students reported familiarity with adult ADHD, yet a significant segment remained oblivious to their own potential symptoms. This disparity is compounded by the demanding nature of medical education that may exacerbate ADHD symptoms and hinder academic achievement.
Implications of Findings
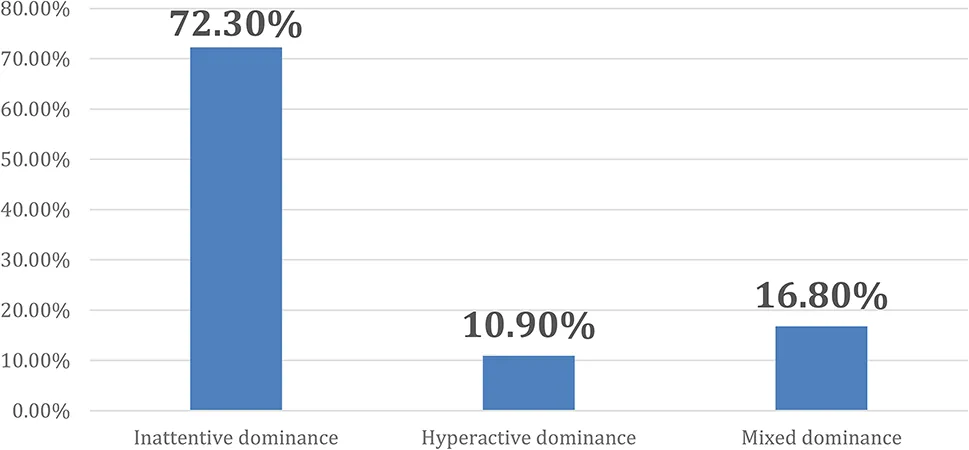
The implications of these findings are critical: undiagnosed ADHD can lead to severe ramifications including decreased academic performance, heightened anxiety, and compromised future relationships as students try to navigate the rigors of medical training. An enormous 72.3% of those identified with undiagnosed ADHD presented with inattentive symptoms, which often go unnoticed, leaving these students without any support or intervention.
Cultural Factors and Underdiagnosis
Cultural factors play a pivotal role in the underdiagnosis of ADHD in Pakistan, where awareness and mental health resources lag behind. Unlike some global contexts where ADHD is actively screened, the reality in Pakistan may leave many students without a proper diagnosis. Furthermore, the study highlighted how the overlap of ADHD symptoms with other psychiatric conditions, such as anxiety and depression, often muddies the diagnostic waters, leading to increased stigma and misinformation within medical circles.
Demographic Correlations
The research also uncovered interesting demographic correlations, such as a notable association between ADHD and coexisting psychiatric disorders among affected individuals. The findings emphasized that family history significantly influences the likelihood of developing ADHD, reaffirming previous studies on its hereditary nature, where having a family member with ADHD increases the risk by a staggering 15% to 60%.
Call to Action
Critically, as education surrounding adult ADHD evolves, there is an urgent need for targeted campaigns to raise awareness among medical students. By addressing misconceptions and biases surrounding ADHD, universities can create a supportive environment conducive to early identification and treatment. Improving the knowledge of medical students about ADHD can not only assist them in recognizing their own symptoms but will ultimately shape more empathetic healthcare providers equipped to support future patients.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study reveals urgent and actionable insights into the prevalence of undiagnosed ADHD among medical students in Pakistan. As the academic world grapples with this hidden epidemic, understanding ADHD as a significant public health concern is paramount. This revelation urges not only educators but also policymakers to reinforce frameworks that improve mental health awareness and child and adult ADHD intervention strategies—this is the call to action for a healthier future in medicine.
Stay tuned for more updates as we continue to uncover the hidden challenges faced by medical professionals in training!






 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)