Unlocking the Secrets to Better Health: How Collaborative Networks Could Save Lives
2024-11-25
Author: Emily
As our healthcare systems grapple with public health challenges such as soaring suicide rates and the increasing prevalence of chronic illnesses, groundbreaking research from Indiana University offers a promising solution — a more interconnected understanding of human health.
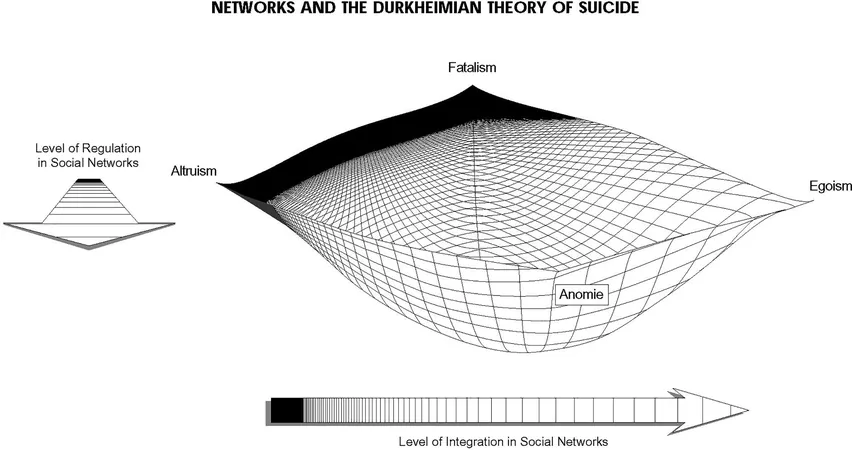
In a pioneering study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Bernice Pescosolido, a Distinguished Professor of Sociology at Indiana University Bloomington, introduces a transformative framework known as the Network Embedded Symbiome (NES). This innovative approach underscores the critical role of collaborative networks—such as family, friends, and community connections—in shaping health outcomes.
Pescosolido argues that a comprehensive understanding of health must include not only biological factors—like genetics and lifestyle—but also the intricate web of interactions across numerous networks that significantly affect well-being. This groundbreaking perspective could revolutionize how researchers tackle diseases, develop policies, and craft health interventions.
"Human health transcends biological confines; it's deeply intertwined with social connections," Pescosolido explains. "The NES framework could shed light on why some communities flourish while others face devastating crises like suicide. It helps identify health problems while also charting pathways towards improved health through network-based interventions."








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)