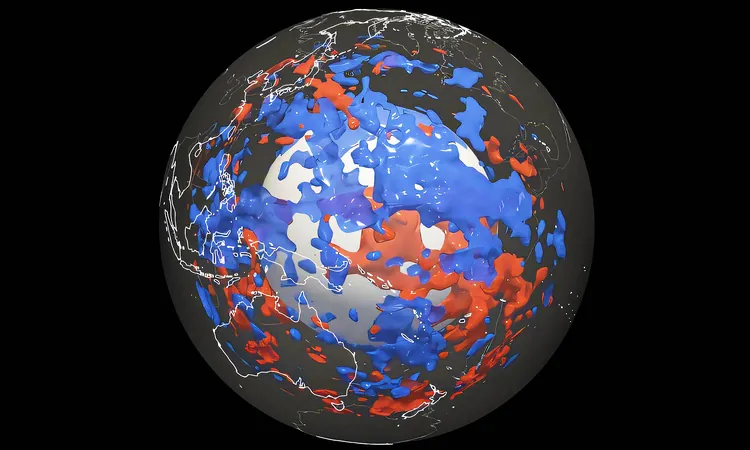
Unveiling Earth's Hidden Secrets: Surprising Discoveries in the Pacific Mantle
2025-01-11
Author: Lok
The Mantle: Earth's Backbone
The mantle, which lies beneath the Earth's crust and above its core, constitutes about 84% of the planet's volume and extends nearly 1,800 miles (2,900 kilometers) deep. It is primarily composed of silicate minerals rich in iron and magnesium, exhibiting a solid yet fluid-like behavior over geological timescales. The slow convection currents resulting from heat from the Earth's core are the driving forces behind tectonic plate movements, which shape our planet's geography through earthquakes and volcanic activity.
A Breakthrough in Seismic Technology
Recent findings are the result of the full-waveform inversion technique, a cutting-edge method that analyzes every seismic wave generated by earthquakes instead of focusing on just one type. By applying this technique to the lower mantle, researchers discovered pockets of material that appear to be remnants of tectonic plates, even in regions where historical subduction has not been documented.
The Origins of the Anomalies
The team observed an array of intriguing anomalies, including one particular zone beneath the western Pacific, which has no evident geological history supporting the presence of old plate fragments. Schouten remarked, “These zones in the Earth’s mantle are much more widespread than we previously thought.”
Implications for Plate Tectonics
If these hidden zones are confirmed to exist more widely beneath the surface, it could lead to a major overhaul of theories related to mantle convection and the formation of geological features. Understanding these anomalies is crucial as it may change our comprehension of how tectonic plates evolve and interact over time.
Continuing the Journey of Discovery
As the mystery of Earth's lower mantle unfolds, advancements in computational technology will allow scientists to analyze even larger datasets, leading to increasingly detailed images of the Earth's hidden layers. Each discovery not only deepens our understanding of planetary geology but also highlights that in the realm of Earth sciences, knowledge is constantly evolving.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)