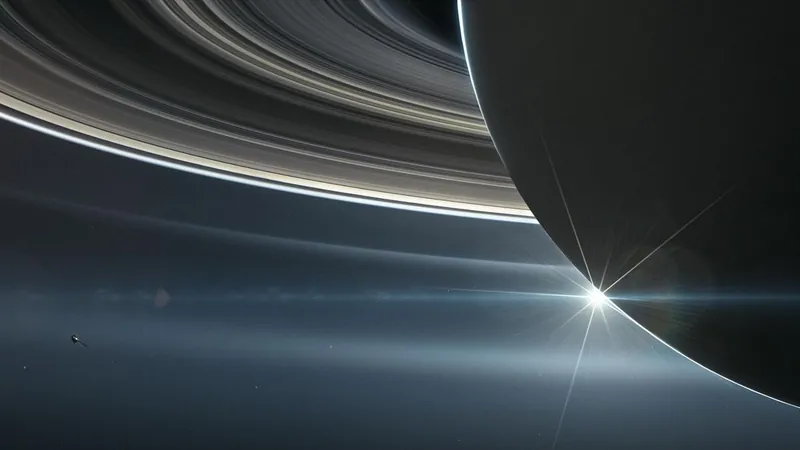

Are Saturn’s Rings Older Than We Thought? Shocking New Study Challenges Conventional Wisdom!
2024-12-17
Author: Sarah
Introduction
A groundbreaking new study has thrown the origins of Saturn's rings into turmoil, suggesting they could be billions of years old, despite their seemingly youthful appearance.
The Enigma of Saturn's Rings
Saturn's iconic rings are one of the solar system's most mesmerizing features, composed of countless ice particles, ranging in size from tiny grains of sand to massive mountains. NASA has long been fascinated by these dazzling rings, but the question of their age and origin has remained a perplexing mystery for scientists.
Historical Perspectives
Historically, many researchers believed that Saturn's rings were relatively young, having formed only about 100 million years ago, during the dinosaur era. This theory was largely based on the rings' pristine condition, which led scientists to think they hadn’t been significantly affected by collisions with micrometeoroids over billions of years. However, a game-changing study published in *Nature Geoscience* argues otherwise.
Debunking Previous Beliefs
Lead author Ryuki Hyodo, a planetary scientist at the Institute of Science Tokyo, contends that the rings’ clean look is deceiving. His research reveals that micrometeoroids, which are tiny space rocks that could potentially soil the rings, don't stick to them upon impact. In fact, when micrometeoroids collide with the icy rings, they vaporize due to the high-energy impact, thus failing to leave any residue.
Implications of the Study
Hyodo explains, “A clean appearance does not necessarily mean the rings are young.” Instead, the study posits that Saturn’s rings might have originated 4.5 to 4 billion years ago, during a time when our solar system was still in a chaotic state, teeming with the movement and interactions of large planetary bodies.
Research Methodology
To probe the nature of Saturn's rings further, Hyodo’s team conducted advanced computer simulations that illustrated the catastrophic conditions of micrometeoroid strikes. These simulations revealed that collisions could reach staggering temperatures of nearly 18,000 degrees Fahrenheit (10,000 degrees Celsius), leading to vaporization rather than particulate contamination of the rings.
The Role of Vaporized Material
In a dramatic twist, the vaporized material could evolve into charged nanoparticles and ions that either escape into space or get absorbed by Saturn, leaving the rings sparkling clean. This ensures the rings maintain their youthful appearance while potentially being billions of years old!
Ongoing Debate
Yet, the debate surrounding the age of Saturn’s rings is far from settled. Sascha Kempf, an associate professor at the University of Colorado Boulder, maintains that his own research indicates the rings are no older than 400 million years. Kempf argues that the methods used in Hyodo’s study do not provide a complete picture.
Future Research
Interestingly, Lotfi Ben-Jaffel, a researcher at the Paris Institute of Astrophysics, has commended Hyodo’s work as a step forward. However, he underscores that more sophisticated modeling is needed to nail down the rings' age accurately.
Conclusion
As researchers continue to dive deeper into the mysteries of Saturn's stunning rings, the quest for answers promises to reveal astonishing insights about the evolution of planetary systems in our universe. Will we soon uncover the truth behind these cosmic marvels, or will the debate continue to rage on? Stay tuned for more incredible discoveries!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)