
Breakthrough in Type 2 Diabetes Management: Virtual Tools Slash Blood Sugar Levels!
2025-04-02
Author: Arjun
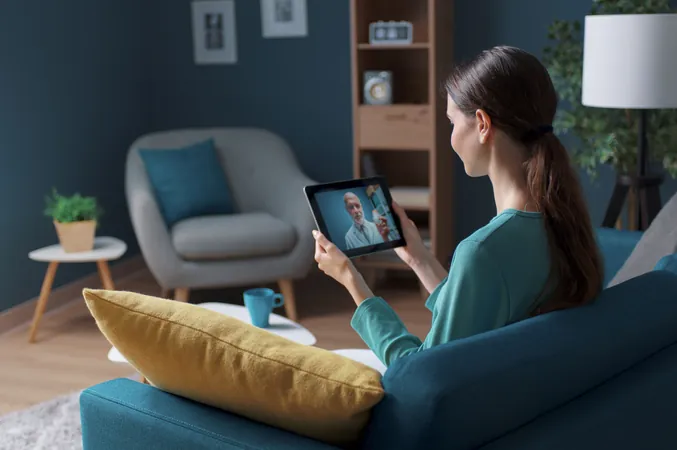
A groundbreaking study from Texas A&M University has unveiled that cost-effective virtual self-management tools for type 2 diabetes (T2D) can significantly lower critical blood sugar levels, marking a new era in diabetes care! Published in *Frontiers in Public Health*, the study's findings highlight the effectiveness of various online interventions that could transform the way patients manage their condition.
Dr. Marcia Ory, a prominent figure at the Texas A&M School of Public Health, stated, “Previous studies have seldom investigated the effectiveness of diabetes self-management based on how interventions are delivered or their combinations.” The current research aimed to fill this gap, focusing on whether patients could benefit from different self-management approaches, particularly when paired together.
The study involved 189 adults aged 25 and older in Texas, all diagnosed with T2D and exhibiting baseline hemoglobin A1c levels of 7.5 or higher. Curiously, approximately 35% of participants hailed from rural regions, demonstrating the broad applicability of these interventions.
Researchers explored three types of interventions: the virtual Making Moves With Diabetes (vMMWD) program, technology-based education and support (TBES), and a combination of both. Each intervention was conducted over three months with evaluations at three and six-month intervals.
The vMMWD program featured personalized 1-on-1 counseling, along with 6 to 8 hours of virtual asynchronous training facilitated by a registered nurse or dietitian. On the other hand, the TBES intervention utilized a user-friendly smartphone app, offering users direct access to a diabetes coach for tailored guidance. Patients benefiting from both interventions received the vast advantages of combined educational tools and support systems.
The results were remarkable, with participants experiencing significant reductions in their A1c levels at both follow-up points. The average drop was about 0.5 points every three months, showcasing that these interventions were effective across both urban and rural populations. Notably, older patients and those in good health reported even greater improvements, while financial stability and higher education levels were linked to better management of blood sugar levels.
Dr. Ory emphasized the lasting implications of the study, asserting that their longitudinal research indicated sustained lower A1c levels over time, unlike many previous studies. This revelation points to the potential for self-paced training and skill development to yield long-term benefits, regardless of how the training is delivered.
This study could be a game changer for millions living with type 2 diabetes, showing that with the right tools and support, effective self-management is within reach. As the world grapples with rising diabetes rates, the implementation of such accessible virtual technologies may pave the way for healthier futures for many.
Stay tuned as researchers continue to explore innovative ways to combat diabetes, empowering patients with the knowledge and resources they need to take control of their health!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)