Drowning in Danger: The Hidden Dilemma of Coagulation Disorders in Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome
2025-04-11
Author: Mei
Exploring the Lethal Link Between SFTS and DIC
In a startling revelation, researchers have uncovered the critical relationship between disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS), a deadly viral illness that has emerged as a significant threat since its first reporting in China in 2009. With incidences gradually spreading across neighboring countries like Korea, Japan, and Vietnam, understanding DIC in the context of SFTS has become a pressing necessity.
What is SFTS?
Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome is caused by the SFTS virus, primarily transmitted through tick bites or exposure to bodily fluids of infected animals. Patients often present with nonspecific symptoms such as fever, headaches, and nausea. However, the condition can escalate rapidly, leading to severe complications including multi-organ failure and, alarmingly, DIC.
The Disconcerting Discovery: DIC's Role in SFTS Outcomes
A recent study involving 246 patients at Zhongnan Hospital has shed light on the sobering statistics surrounding DIC in SFTS patients. Out of those examined, a staggering 12.2% were diagnosed with DIC, a condition marked by abnormal clotting that paradoxically leads to serious bleeding. This group displayed significantly elevated levels of various clinical markers, indicating a higher risk of severe outcomes.
The Grim Reality of Mortality
The findings reveal that patients suffering from DIC experienced a significantly lower survival rate compared to those without it. In fact, the study suggests that DIC is an independent predictor of in-hospital mortality among SFTS patients, with cumulative survival rates plummeting to as low as 46.7% for those with DIC.
What Makes DIC So Dangerous?
DIC is not merely a complication; it’s a complex pathological process that kills through a combination of extensive coagulation factor breakdown and uncontrolled bleeding, leading to potential organ failure. In SFTS, this condition can manifest in dire neurological symptoms and hemorrhagic events, further complicating the already frail health of infected individuals.
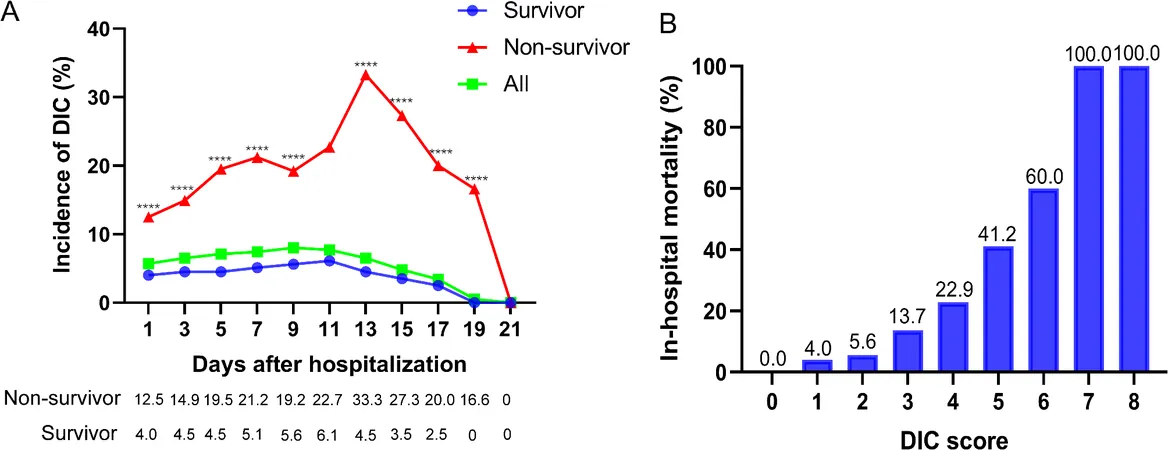
Critical Findings Highlighting the Need for Vigilance
The study elucidates that the incidence of DIC in severely ill patients reached its peak around the 13th day of hospitalization, underscoring the critical time frame for intervention. Coagulation tests revealed alarming trends: deterioration in those with heightened DIC scores correlating with higher mortality—pointing to the desperate need for early detection and management.
Treating the Unseen Enemy
Patients diagnosed with DIC required more aggressive treatments, including invasive mechanical ventilation and plasmapheresis, emphasizing the necessity for swift medical action in the presence of such complications. The alarming contrast in treatment effectiveness further emphasizes DIC’s profound impact on survival rates.
Conclusion: The Urgency for Awareness and Action
As staggering as the findings are, they serve as a clarion call for the medical community: understanding and recognizing DIC in SFTS patients is crucial in improving prognoses. With ongoing surveillance and research, the hope remains to significantly reduce the mortality risks associated with this enigmatic yet perilous complication.
Together, let's bring attention to the often-overlooked ramifications of SFTS and DIC, paving the way for better diagnostic methods and treatment protocols.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)