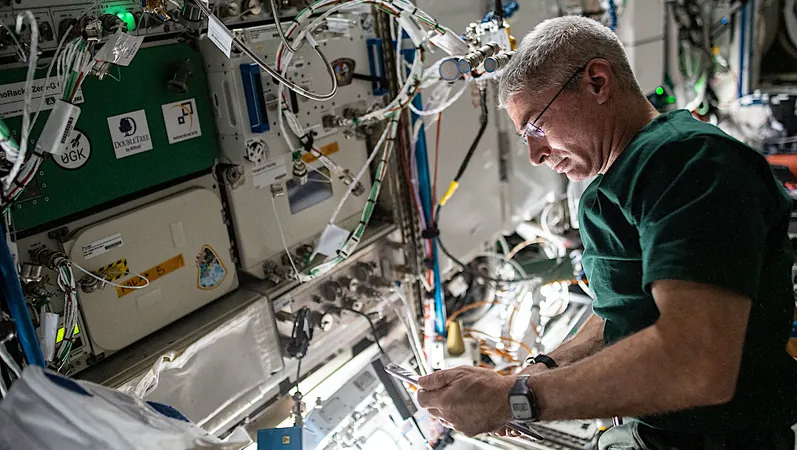

Groundbreaking Findings from NASA's Space Life Science Research: A Gateway to Intergalactic Exploration
2024-10-07
Author: Mei
NASA's Innovative Research on Life in Space
NASA has recently unveiled exciting new research stemming from the International Space Station (ISS) that throws light on the adaptations of life in outer space. This crucial research not only aims to extend human presence beyond Earth but also promises to deepen our understanding of some complex biological processes.
Microbial Adaptations to Space Conditions
One of the standout studies was spearheaded by a team, including Szydlowski and Venkateswaran, focusing on novel bacterial species isolated from the ISS. Their findings, published in the journal *Microbiome*, illustrate how these microbes adapt to the unique conditions of space. Understanding their functional gene annotations through comparative genome analysis could have significant implications for life support systems on long-duration missions, such as those to Mars. The profound implications of this research could enable astronauts to utilize these microbes to assist in waste recycling and oxygen generation - a game-changer for off-Earth living!
Enhancing Astronaut Metabolic Health
Moreover, research led by Patterson and his colleagues examined the impact of sitting interruption strategies on metabolic health in postmenopausal women, revealing that such modalities could enhance metabolic function post-meal. This study offers valuable insights into maintaining astronaut health during lengthy missions where sedentary behavior is unavoidable.
The Future of Space Agriculture
As space agriculture becomes pivotal for future interplanetary missions, research on nitrogen accounting, as explored by Yates et al., opens new avenues. Their model addresses the nutritional complexities of growing a variety of crops in space, essential for building a sustainable food supply. This advancement boosts the potential of producing food that is both nutritionally diverse and efficient in resource utilization - a necessity for exploring habitats beyond our home planet.
Neurological Well-being Through Eye Tracking
In the realm of physical health, a notable editorial from Cecchetti and Roy proposes the use of eye tracking as a potential biomarker for neurological conditions which may be exacerbated in space. This research could facilitate early detection and treatment strategies for astronauts, ensuring their well-being during missions that push the boundaries of human endurance.
Cardiovascular Health in Microgravity
Furthermore, while research on managing the cardiovascular effects of extended spaceflight continues, recent studies indicate that humans may exhibit signs of cardiovascular aging after just one month in a microgravity environment. This finding, published in *Nature*, highlights the urgent need for protective strategies to counteract spaceflight-induced health issues.
Innovation in Tissue Engineering
Additionally, significant advancements in tissue engineering were reported, showcasing the feasibility of 3D bioprinting organic tissues like meniscus tissues aboard the ISS. Such capabilities could revolutionize medical interventions that astronauts may require during their voyages.
Tailored Health Interventions for Astronauts
As we strive for deeper space exploration, studies delving into the health impacts of microgravity on cells, like the research from Igbineweka, reveal how space affects red blood cells, specifically in sickle cell disease. This underscores the need for tailored health interventions for diverse astronaut populations.
Conclusion: Paving the Way for Human Life Beyond Earth
With each new discovery, NASA continues to pave the way for sustainable human life beyond Earth, bringing us a step closer to realizing our dreams of venturing through the cosmos. This comprehensive body of research exemplifies the multidimensional challenges and innovations ahead as humanity seeks to explore and possibly inhabit other worlds. Keep following these developments, as they could signal the dawn of a new chapter in human exploration!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)