Groundbreaking Research Reveals New Insights into Mental Disorder Detection Using fMRI Scans
2024-11-21
Author: Rajesh
Introduction
Newly published findings from a team at Georgia State University are making waves in the field of neuroscience, as they unveil groundbreaking methods to identify key signatures of mental disorders, particularly schizophrenia, through advanced fMRI scans. The study has been featured in the prestigious journal *Nature Mental Health*, highlighting its significant implications for early diagnosis and treatment.
Key Discoveries
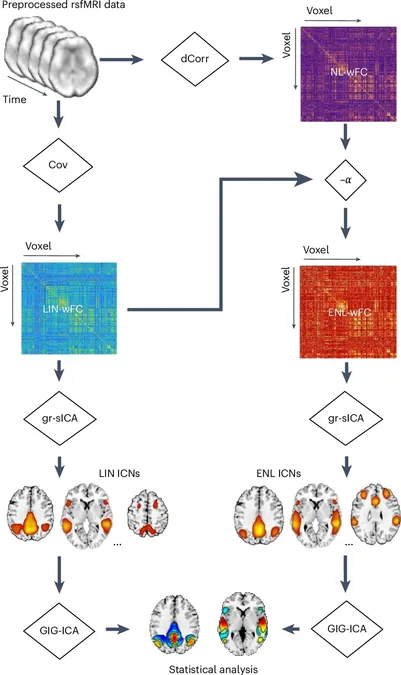
The research team has discovered unique brain connections exhibiting distinct spatial variations that are particularly pronounced in patients diagnosed with schizophrenia. Distinguished University Professor of Psychology, Vince Calhoun, a principal investigator on this pivotal study, stated, “This research marks an exciting leap forward, offering an entirely new lens to capture the complex, hidden fluctuations within functional brain networks.”
Traditionally, studies have focused on linear relationships within brain connectivity, which can overlook critical nonlinear patterns. This latest research counters that trend by introducing a method that extracts detailed maps of large-scale brain networks, revealing a new dimension of human brain organization. The findings indicate that these nonlinear connections can effectively differentiate individuals with schizophrenia from healthy controls, uncovering aspects that remain concealed through conventional methods.
Insights from Researchers
“In focusing on nonlinear relationships—often neglected in traditional neuroimaging—we reveal structured spatial patterns that offer insights into brain network functionality,” explained Calhoun. “Crucially, these patterns exhibit disruptions in individuals with schizophrenia, even when typical linear connections appear to be intact.”
The study also features contributions from third-year Ph.D. student in neuroscience, Spencer Kinsey, who emphasized the innovative statistical methods employed. “We discovered these new functional brain connectivity patterns by using techniques that extend beyond the linear frameworks commonly explored in current studies,” Kinsey stated.
Future Implications
The lead principal investigator, Armin Iraji, assistant professor of computer science and neuroscience, reflected on the decade of research that paved the way for this discovery: “We are poised to unlock the brain’s secrets and uncover hidden intrinsic patterns that could revolutionize our understanding of mental disorders, aging, neurodegenerative diseases, and more.”
These advancements may lead to the identification of potential biomarkers for schizophrenia, which can have profound implications for early diagnosis and tailored interventions. As Calhoun remarked, “This discovery brings us closer to identifying a brain-based biomarker for schizophrenia, which could change the landscape of how we approach mental health treatment.”
Collaborative Efforts
The TReNDS Center, a collaborative effort between Georgia State University, Georgia Institute of Technology, and Emory University, is dedicated to pioneering the development and application of innovative analytical techniques and neuroinformatics tools aimed at transforming brain imaging data into actionable biomarkers for mental health issues.
Conclusion
As researchers continue to peel back the layers of the brain’s complexities, the future of mental health diagnosis and treatment looks increasingly promising, ushering in new possibilities for interventions that could significantly improve patient outcomes. Stay tuned for more updates on how this groundbreaking research will shape the future of mental health diagnostics!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)