Innovative Airlock Design to Safeguard Mars from Earth Microbes During Human Exploration
2024-12-08
Author: Rajesh
Innovative Airlock Design to Safeguard Mars from Earth Microbes During Human Exploration
As humanity inches closer to setting foot on the Red Planet, the urgency to shield Mars from contamination by Earth’s microbes has reached a critical point. This concern is paramount not only for preserving Martian ecosystems but also for ensuring the integrity of scientific inquiries into the potential for indigenous life.
Presently, the technological frameworks in place for planetary protection primarily cater to uncrewed missions. However, with numerous space agencies and commercial players racing to launch crewed missions to Mars, a significant disconnect has emerged between these ambitious timelines and the necessary protective measures. A new research paper aims to bridge this gap, proposing a groundbreaking solution tailored specifically for human explorers.
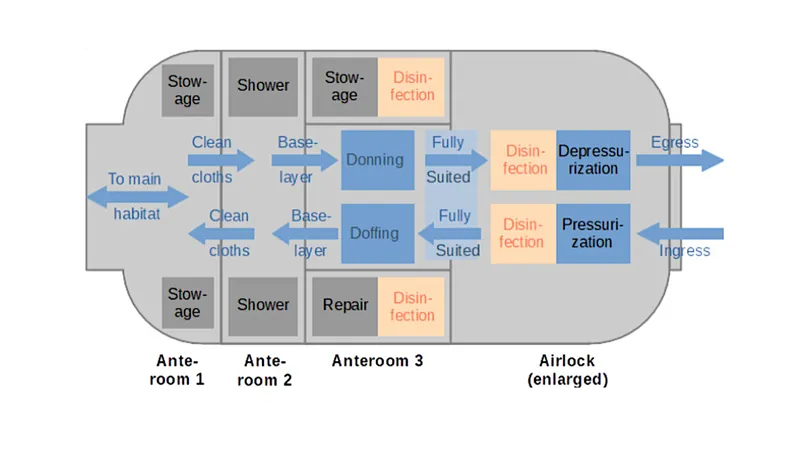
Central to the risk of contamination is the moment astronauts transition from their habitats to the Martian surface. This activity is viewed as the most significant threat of introducing earthly microbes onto Mars. To counteract this risk, researchers propose a novel design for airlocks with a focus on planetary protection.
The proposed airlock system features a sturdy design comprised of two pressure-tight doors with a central compartment split into three distinct, airtight zones:
1. Suit-Up Area
Where astronauts can prepare their Extravehicular Activity (EVA) suits, make repairs, and store their equipment. This area may also include suitports for enhanced efficiency.
2. Hygiene Compartment
Essential for maintaining cleanliness, this space will facilitate showers and other hygiene practices, minimizing microbial transfer.
3. Storage for Indoor Apparel
A dedicated area for housing undergarments and everyday clothing, ensuring that only specialized gear is worn outside, further reducing contamination risks.
Remarkably, while many of these functionalities are already necessary in habitat modules, the proposed airlock consolidates them into a single entity. This integration not only simplifies operations but also strengthens protective measures against biological contamination.
With the mission to explore Mars ramping up, these advancements could play a pivotal role in humanity's quest to understand our neighboring planet while safeguarding it from potential environmental disruptions. The future of Mars exploration hinges on solutions like this, ensuring that our search for life beyond Earth does not inadvertently compromise another world.
For a detailed overview of this airlock concept and its implications for planetary protection, refer to the research published in NPJ Microgravity on October 7, 2023.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)