Legal Hurdles Delay Vital Mpox Vaccines for Children in Congo: What You Need to Know
2024-11-26
Author: Yu
Introduction
In a significant public health initiative, vaccinations against mpox have begun for adults in Kinshasa, the capital of the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). However, the most vulnerable group—children—are still waiting as a crucial vaccine donation from Japan is being held up by legal complications.
Japan's Vaccine Donation
Japan's government pledged to donate three million doses of LC16m8, a vaccine originally developed for smallpox by KM Biologics, specifically designed for use in children. This donation represents the largest single contribution to combat mpox globally, highlighting Japan's commitment to addressing health crises.
Legal Complications
Nevertheless, a sticking point in negotiations emerged concerning liability for any unexpected side effects of the vaccine. This has been a recurring issue in global health partnerships, particularly for poorer nations that may face significant financial consequences without adequate agreements in place. Congo's health minister, Samuel Roger Kamba Mulamba, explained that this delay stemmed from concerns about who would be financially responsible should adverse reactions occur following vaccination. Fortunately, he announced that the associated legal issues had now been resolved, paving the way for the vaccine delivery.
Urgent Need for Improved Frameworks
Despite this progress, the delay underscores the urgent need for improved frameworks governing international health donations, particularly in emergencies like the current mpox outbreak. Experts argue that well-structured no-fault compensation systems are essential during health crises to accelerate vaccine distribution without fear of liability.
Challenges of Approval
Adding to the complexity, while the LC16m8 vaccine received "emergency use" clearance from the World Health Organization and DRC’s government, there are challenges regarding the insurance coverage for adverse effects linked to vaccines that are approved via expedited processes. In contrast, the Bavarian Nordic vaccine, which is also being administered to adults, has received fuller approvals and does not face these issues.
Current Vaccine Distribution Challenges
Currently, the U.S. and other nations have pledged around three million doses of the Bavarian vaccine to DRC, but only a fraction has been delivered. Health officials are observing a slow rollout of vaccinations within at-risk communities, exacerbated by a lack of awareness about available vaccines—an issue that may equally impede the distribution of the Japanese donation for children.
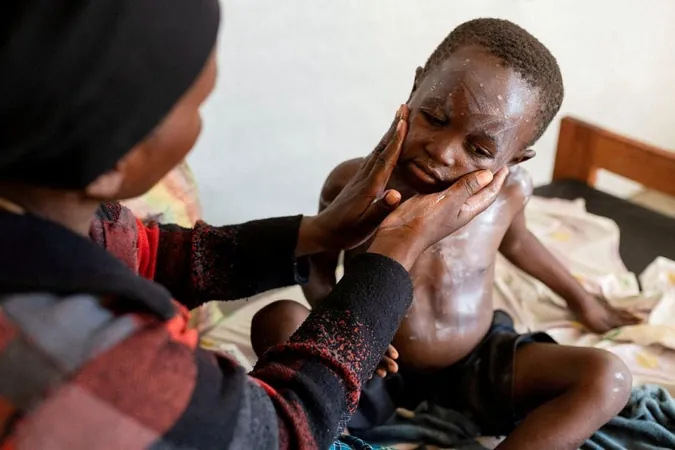
Impact on Children
It’s worth noting that this year's mpox outbreak has disproportionately affected children, who represent the majority of the over 1,100 suspected mpox-related deaths reported in Africa so far. Doctors in the region are urging a swift arrival of the vaccines, emphasizing the importance of implementing strategic administration plans and effective communication within communities.
Vaccination Techniques and Training
The LC16m8 vaccine requires a specialized bifurcated needle technique that necessitates training for healthcare personnel. Japan is set to donate these needles alongside the vaccine doses, further stressing the need for proper training to ensure effective vaccination campaigns.
Conclusion
As the situation unfolds, the Japanese government has expressed its commitment to addressing and coordinating solutions to these obstacles. As one official indicated, immediate resolutions may be complex, but efforts are underway to expedite the process. The health outcomes of hundreds of children hang in the balance, and as global and local health authorities strategize, the focus remains on delivering solutions swiftly to combat this deadly disease.





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)