New Benchmarking Study Empowers Researchers in Spatial Transcriptomics Data Analysis
2024-10-10
Author: Wei
Introduction
In a groundbreaking move for the scientific community, a team of researchers from Vanderbilt University has unveiled a comprehensive benchmarking study designed to guide scientists in choosing the most effective methods for analyzing spatial transcriptomics (ST) data. This innovative study, spearheaded by Dr. Xin Maizie Zhou, an assistant professor specializing in biomedical engineering and computer science, was recently published in the esteemed journal *Genome Biology*.
What is Spatial Transcriptomics?
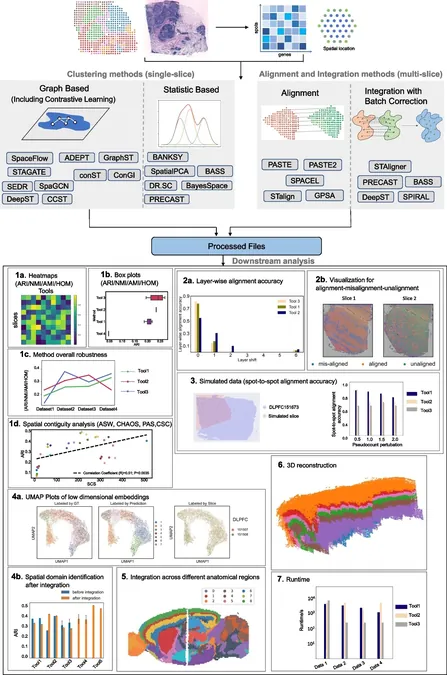
Spatial transcriptomics is a cutting-edge technology that enables scientists to map gene expression patterns within tissues while maintaining their spatial context. This involves slicing tissue samples and placing them on specialized slides embedded with spatially indexed barcodes. During processing, ribonucleic acid (RNA) from specific tissue locations is captured by these barcodes, allowing for detailed mapping of gene expression back to its original anatomical site. This powerful technique has revolutionized the study of complex tissues since its broader adoption in 2020, with significant implications in fields like cancer research and neuroscience. Researchers can investigate how gene expression varies in different regions of the brain, shedding light on regional functions and disease mechanisms.
The Challenge of Diverse Analytical Tools
Despite its immense potential, the diversity of analytical tools available for processing ST data can be daunting for researchers. The sheer volume of options can obscure which methods are best suited for particular research objectives, posing a significant challenge in this rapidly evolving field.
The Benchmarking Study
To tackle this issue, the Vanderbilt team rigorously evaluated 16 clustering methods, five alignment methods, and five integration methods across various datasets. Their comparative analysis produced vital recommendations that will aid researchers in selecting the optimal tools for their specific projects in spatial transcriptomics.
Conclusion
Our aim was to create a straightforward and accessible resource for researchers as they navigate the complex landscape of spatial transcriptomics analysis,” remarked Dr. Zhou, who is actively engaged with Vanderbilt's trans-institutional Data Science Institute. The team hopes that this benchmarking study will serve as a valuable asset for scientists eager to advance their understanding through the lens of spatial transcriptomics.
Future Implications
With this study, researchers can now confidently explore the intricacies of gene expression in tissues, unlocking new pathways to understanding diseases and driving future innovations in biomedical research. As the field continues to grow, this resource affirms Vanderbilt University’s commitment to enhancing scientific collaboration and discovery. Stay tuned as we follow the Thrilling Journey of Spatial Transcriptomics and its potential to unravel complex biological puzzles!





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)