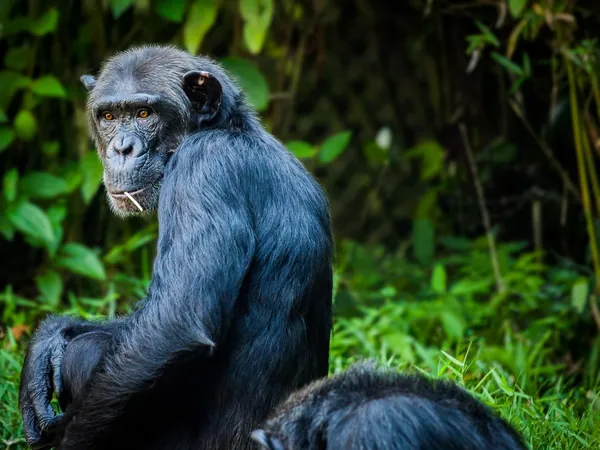

Groundbreaking Discovery: Full Genome Sequences of Six Ape Species Revealed!
2025-04-12
Author: Siti
Revolutionary Insights into Primate Genetics!
In a groundbreaking study led by an international team from Penn State, the National Human Genome Research Institute, and the University of Washington, new genomic revelations about seven ape species, including humans, are turning our understanding of genetics upside down!
This ambitious research unveiled what are known as "complete" reference genomes—comprehensive genetic blueprints that allow for unprecedented comparisons across species and highlight alarming variations that could affect health and survival.
Unlocking Evolutionary Secrets!
Previously hampered by technological limitations, researchers have now assembled full DNA sequences along each chromosome, revealing intricate details that shed light on primate evolution and uncover novel species-specific genes.
According to Christian Huber, a biology assistant professor at Penn State, these significant findings showcase adaptive signatures related to diet, immune responses, and cellular activity, providing vital insights into the evolutionary forces that shaped great ape genomes.
A New Era in Genomic Research!
The new complete genomes surpass previous references in accuracy and completeness, offering deeper insights into genetic functions tied to health. These revelations could pave the way for advancements in conservation genetics, ultimately helping to protect endangered ape species and furthering our understanding of human evolution.
Kateryna Makova, co-senior author of the study, hailed this work as a milestone, stating it allows for a richer understanding of genomic evolution that was previously impossible with incomplete data.
Decoding the Genomes: A Familiar Face in a New Context!
The human genome was initially sequenced back in 2001, and researchers have since aimed to sequence other ape genomes to illuminate the evolutionary history behind our own genetic makeup. This research is crucial for crafting effective conservation strategies for endangered species.
Using cutting-edge sequencing techniques, the team successfully decoded the genomes of six ape species—chimpanzee, bonobo, gorilla, Bornean orangutan, Sumatran orangutan, and siamang—substantially enhancing our genetic map.
New Genes, New Insights!
Researchers utilized advanced long-read sequencing technologies to read extensive DNA segments, assembling them flawlessly from one chromosome end to the other. This process unveiled previously unidentified genes that could partly explain the unique traits among species, including those that may define human intelligence.
Exploring the Unknown Regions of DNA!
Their pioneering work identified vital evolutionary markers and tapped into inaccessible genome regions, revealing a treasure trove of sequences forming non-canonical DNA structures.
These unusual arrangements do not conform to the typical double-helix structure and are believed to regulate essential cellular processes. Some of these structures are even linked to diseases like cancer.
The Future of Genomic Research!
Previous genome versions were incomplete due to outdated methods of assembly, akin to assembling a 2,000-piece puzzle without a guiding image. However, advancements in DNA sequencing technologies and refined computational algorithms have expeditiously transformed this landscape.
The public can access the treasure trove of data generated by these reference genomes online, marking the dawn of a new chapter in genomic research.
Looking forward, the team plans to broaden this high-quality sequencing approach to gather more data on individual apes within the studied species and explore new species, including gibbons.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)